Overview
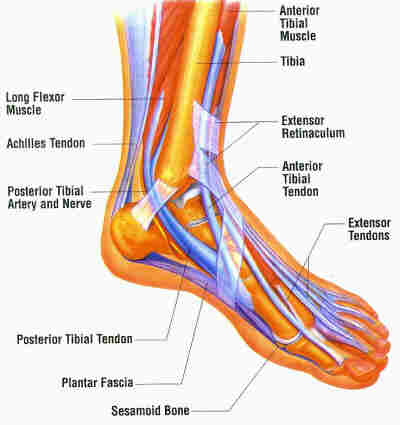
The condition of flat feet in adults is known as ?fallen arches.? Not all adults develop flat feet, and some people are more prone to developing the condition than others. An obese person puts extra weight on their feet while walking or standing. Over time, this can weaken the components that make up the arch and cause the arch to collapse. A woman who is pregnant may also suffer from flat feet during her pregnancy. The problem with developing flat feet as an adult is that in most cases the changes are permanent, if not bothersome. Doctors recommend using custom-made orthotics in shoes to treat the problem. Flat feet were once considered a result of poor health, but it has been proven that athletes such as runners, who are in great condition, also suffer from flat feet. In fact, it?s very common among track runners. Flat feet were once thought of as a bad thing. But studies show that people with higher arches are four times more likely to injure or sprain their ankles than people with flat feet. Studies conducted by the military have discredited the idea that flat feet are a reason to be excused from service.
Causes
Fallen arches may be caused by a number of causes, including increased elastin during pregnancy, arthritis, injury, excessive stress on the foot, fused bones in the foot, or an extra bone. They may cause not only foot pain, but also pain in the legs, knees, and back and a loss of mobility. The condition is most often treated with orthotics, structures placed in the shoes to support the feet, but this may not be enough for severe cases. Exercises to strengthen and rebuild the arches can also be helpful. Surgery is sometimes the best method of treatment, as it can completely rebuild the arches and has lasting results, but it is quite expensive and considered a last resort.
Symptoms
Pain and stiffness of the medial arch or anywhere along the mid-portion of the foot. Associated discomfort within and near the ankle joint. The knees, hips, and lower back may be the primary source of discomfort. Feet may often feel tired and achy. Painful shin splints may develop with activity. Gait may be awkward.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists are trained in expertly assessing flat feet and identifying different risk factors and the causes for it. Initial assessment will begin with a detailed history attempting to find out if any underlying illness has resulted in this. A detailed clinical examination normally follows. The patient may be asked to perform certain movements such as walking or standing on their toes to assess the function of the foot. Footwear will also be analysed to see if there has been excessive wear or if they are contributing to the pronation of the foot. To assess the structure of the foot further, the podiatrist may perform certain x-rays to get a detailed idea of the way the bones are arranged and how the muscle tissues may be affecting them. It also helps assess any potential birth defects in a bit more detail.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
The type of treatment will depend on the stage of PTTD present. There are four stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Stage I. The posterior tibial tendon is inflamed but has normal strength. There is little to no change in the arch of the foot. The patient can still perform a single-limb heel rise and has a flexible hindfoot. Orthotic treatment options include modified off the shelf inserts and custom molded orthotics. Stage 2. The tendon is partially torn or shows degenerative changes and as a result loses strength.There is considerable flattening of the arch without arthritic changes in the foot. The patient cannot perform single-limb heel rise. Pain is now present on the lateral aspect of the ankle. Orthotic treatment is similar as that in stage I, with the addition of more rigid arch supports and wedging. Stage 3. Results when the posterior tibial tendon is torn and not functioning. As a result the arch is completely collapsed with arthritic changes in the foot. A solid ankle AFO is suggested in conjunction with a modified orthopedic shoe. Stage 4. Is identical to stage three except that the ankle joint also becomes arthritic. A rigid AFO and modified orthopedic shoe is required.
Surgical Treatment

A better approach is to strengthen the weakened ligaments with Prolotherapy, supplemented by an arch support if the condition has existed for several years. Chronic pain is most commonly due to tendon and ligament weakness, or cartilage deterioration. The safest and most effective natural medicine treatment for repairing tendon, ligament and cartilage damage is Prolotherapy. In simple terms, Prolotherapy stimulates the body to repair painful areas. It does so by inducing a mild inflammatory reaction in the weakened ligaments and cartilage. Since the body heals by inflammation, Prolotherapy stimulates healing. Prolotherapy offers the most curative results in treating chronic pain. It effectively eliminates pain because it attacks the source: the fibro-osseous junction, an area rich in sensory nerves. What?s more, the tissue strengthening and pain relief stimulated by Prolotherapy is permanent.

The condition of flat feet in adults is known as ?fallen arches.? Not all adults develop flat feet, and some people are more prone to developing the condition than others. An obese person puts extra weight on their feet while walking or standing. Over time, this can weaken the components that make up the arch and cause the arch to collapse. A woman who is pregnant may also suffer from flat feet during her pregnancy. The problem with developing flat feet as an adult is that in most cases the changes are permanent, if not bothersome. Doctors recommend using custom-made orthotics in shoes to treat the problem. Flat feet were once considered a result of poor health, but it has been proven that athletes such as runners, who are in great condition, also suffer from flat feet. In fact, it?s very common among track runners. Flat feet were once thought of as a bad thing. But studies show that people with higher arches are four times more likely to injure or sprain their ankles than people with flat feet. Studies conducted by the military have discredited the idea that flat feet are a reason to be excused from service.
Causes
Fallen arches may be caused by a number of causes, including increased elastin during pregnancy, arthritis, injury, excessive stress on the foot, fused bones in the foot, or an extra bone. They may cause not only foot pain, but also pain in the legs, knees, and back and a loss of mobility. The condition is most often treated with orthotics, structures placed in the shoes to support the feet, but this may not be enough for severe cases. Exercises to strengthen and rebuild the arches can also be helpful. Surgery is sometimes the best method of treatment, as it can completely rebuild the arches and has lasting results, but it is quite expensive and considered a last resort.
Symptoms
Pain and stiffness of the medial arch or anywhere along the mid-portion of the foot. Associated discomfort within and near the ankle joint. The knees, hips, and lower back may be the primary source of discomfort. Feet may often feel tired and achy. Painful shin splints may develop with activity. Gait may be awkward.
Diagnosis
Podiatrists are trained in expertly assessing flat feet and identifying different risk factors and the causes for it. Initial assessment will begin with a detailed history attempting to find out if any underlying illness has resulted in this. A detailed clinical examination normally follows. The patient may be asked to perform certain movements such as walking or standing on their toes to assess the function of the foot. Footwear will also be analysed to see if there has been excessive wear or if they are contributing to the pronation of the foot. To assess the structure of the foot further, the podiatrist may perform certain x-rays to get a detailed idea of the way the bones are arranged and how the muscle tissues may be affecting them. It also helps assess any potential birth defects in a bit more detail.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
The type of treatment will depend on the stage of PTTD present. There are four stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Stage I. The posterior tibial tendon is inflamed but has normal strength. There is little to no change in the arch of the foot. The patient can still perform a single-limb heel rise and has a flexible hindfoot. Orthotic treatment options include modified off the shelf inserts and custom molded orthotics. Stage 2. The tendon is partially torn or shows degenerative changes and as a result loses strength.There is considerable flattening of the arch without arthritic changes in the foot. The patient cannot perform single-limb heel rise. Pain is now present on the lateral aspect of the ankle. Orthotic treatment is similar as that in stage I, with the addition of more rigid arch supports and wedging. Stage 3. Results when the posterior tibial tendon is torn and not functioning. As a result the arch is completely collapsed with arthritic changes in the foot. A solid ankle AFO is suggested in conjunction with a modified orthopedic shoe. Stage 4. Is identical to stage three except that the ankle joint also becomes arthritic. A rigid AFO and modified orthopedic shoe is required.
Surgical Treatment

A better approach is to strengthen the weakened ligaments with Prolotherapy, supplemented by an arch support if the condition has existed for several years. Chronic pain is most commonly due to tendon and ligament weakness, or cartilage deterioration. The safest and most effective natural medicine treatment for repairing tendon, ligament and cartilage damage is Prolotherapy. In simple terms, Prolotherapy stimulates the body to repair painful areas. It does so by inducing a mild inflammatory reaction in the weakened ligaments and cartilage. Since the body heals by inflammation, Prolotherapy stimulates healing. Prolotherapy offers the most curative results in treating chronic pain. It effectively eliminates pain because it attacks the source: the fibro-osseous junction, an area rich in sensory nerves. What?s more, the tissue strengthening and pain relief stimulated by Prolotherapy is permanent.
